稳定排序:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序、基数排序
不稳定排序:选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序
冒泡排序 总共需要比较n - 1趟,每趟n - 1 - i次。
1 2 3 4 5 void bubbleSort (T a[], int n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) for (int j = 0 ; j < n - 1 - i; j++) if (a[j] > a[j + 1 ]) swap(a[j], a[j + 1 ]); }
快速排序 基于分治和递归。
其基本思路是,在数组中选择一个元素作为基准值,然后将数组中小于基准值的元素移动到它的左边,大于基准值的元素移动到它的右边。然后对左右两个子数组递归地重复这个过程,直到子数组的大小为1或0。
是不稳定排序。当要比较的值和基准值一样时,根据代码可能放在基准值左边或右边。
最好情况:每次划分左右两边的元素数量相同各为一半,则此时时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
最坏情况:每次划分所有元素都在一边,另一边为空,则此时与冒泡排序类似,时间复杂度为O(n²)
平均情况:时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
因此关键在于每次基准值的选取。
通过不同方式选取基准值,有以下几种衍生快排:
随机快速排序 :即在数组中完全随机地挑选一个值作为基准值。
三数取中快速排序 :即取数组中第一个、中间、最后一个这三个元素的中位数作为基准值。
三划分快速排序 :适用于数组中有较多大小相同的数。对于等于基准值的数分为除左右外的第三部分,不用继续参与递归。
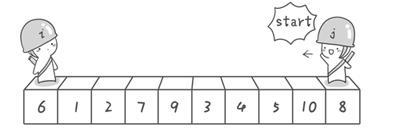
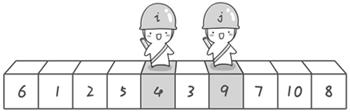
图解:
以数组中第一个元素为基准值
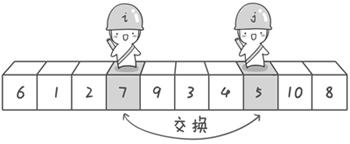
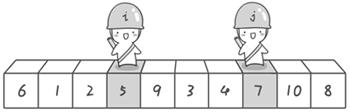
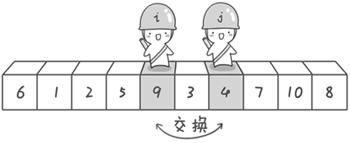
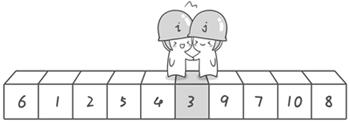
左指针不断右移,直到找到比基准值大的元素停下;右指针不断左移,直到找到比基准值小的元素停下
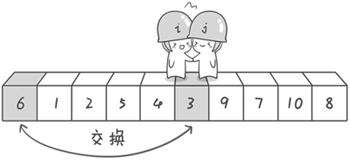
当两指针碰面或超过,说明已经全部遍历了
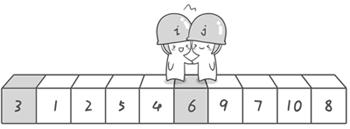
交换后左边都小于基准值,右边都大于基准值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 int partition (T a[], int begin, int end) { int left = begin + 1 ; int right = end; T base = a[begin]; while (true ) { while (a[left++] < base); while (a[right--] > base); if (left >= right) break ; swap(a[left], a[right]); } swap(a[right], a[begin]); return right; } int randomPartition () { int randomIndex = Random(begin, end); swap(a[randomIndex], a[begin]); return partition(a, begin, end); } void quickSort (T a[], int begin, int end) { if (begin < end) { int middle = partition(a, begin, end); quickSort(a, begin, middle - 1 ); quickSort(a, middle + 1 , end); } }
堆排序 平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
最坏时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class HeapSortTest { public int [] heapSort(int [] nums) { buildMaxHeap(nums); int heapSize = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) { int curr = nums[0 ]; nums[0 ] = nums[heapSize - 1 ]; nums[heapSize - 1 ] = curr; heapSize--; adjust(nums, heapSize, 0 ); } return nums; } public void buildMaxHeap (int [] nums) { for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { adjust(nums, nums.length, i); } } public void adjust (int [] nums, int heapSize, int i) { int l = (i + 1 ) * 2 - 1 ; int r = (i + 1 ) * 2 ; int max = i; if (l < heapSize && nums[l] > nums[max]) max = l; if (r < heapSize && nums[r] > nums[max]) max = r; if (i != max) { int curr = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[max]; nums[max] = curr; adjust(nums, heapSize, max); } } }